Repository
Intent
Repository layer is added between the domain and data mapping layers to isolate domain objects from details of the database access code and to minimize scattering and duplication of query code. The Repository pattern is especially useful in systems where number of domain classes is large or heavy querying is utilized.
Explanation
Real world example
Let’s say we need a persistent data store for persons. Adding new persons and searching for them according to different criteria must be easy.
In plain words
Repository architectural pattern creates a uniform layer of data repositories that can be used for CRUD operations.
Repositories are classes or components that encapsulate the logic required to access data sources. They centralize common data access functionality, providing better maintainability and decoupling the infrastructure or technology used to access databases from the domain model layer.
Programmatic Example
Let’s first look at the person entity that we need to persist.
1
2@ToString
3@EqualsAndHashCode
4@Setter
5@Getter
6@Entity
7@NoArgsConstructor
8public class Person {
9
10 @Id
11 @GeneratedValue
12 private Long id;
13 private String name;
14 private String surname;
15 private int age;
16
17 /**
18 * Constructor.
19 */
20 public Person(String name, String surname, int age) {
21 this.name = name;
22 this.surname = surname;
23 this.age = age;
24 }
25
26}
We are using Spring Data to create the PersonRepository so it becomes really simple.
1@Repository
2public interface PersonRepository
3 extends CrudRepository<Person, Long>, JpaSpecificationExecutor<Person> {
4
5 Person findByName(String name);
6}
Additionally we define a helper class PersonSpecifications for specification queries.
1public class PersonSpecifications {
2
3 public static class AgeBetweenSpec implements Specification<Person> {
4
5 private final int from;
6
7 private final int to;
8
9 public AgeBetweenSpec(int from, int to) {
10 this.from = from;
11 this.to = to;
12 }
13
14 @Override
15 public Predicate toPredicate(Root<Person> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb) {
16 return cb.between(root.get("age"), from, to);
17 }
18
19 }
20
21 public static class NameEqualSpec implements Specification<Person> {
22
23 public String name;
24
25 public NameEqualSpec(String name) {
26 this.name = name;
27 }
28
29 public Predicate toPredicate(Root<Person> root, CriteriaQuery<?> query, CriteriaBuilder cb) {
30 return cb.equal(root.get("name"), this.name);
31 }
32 }
33
34}
And here’s the repository example in action.
1 var peter = new Person("Peter", "Sagan", 17);
2 var nasta = new Person("Nasta", "Kuzminova", 25);
3 var john = new Person("John", "lawrence", 35);
4 var terry = new Person("Terry", "Law", 36);
5
6 repository.save(peter);
7 repository.save(nasta);
8 repository.save(john);
9 repository.save(terry);
10
11 LOGGER.info("Count Person records: {}", repository.count());
12
13 var persons = (List<Person>) repository.findAll();
14 persons.stream().map(Person::toString).forEach(LOGGER::info);
15
16 nasta.setName("Barbora");
17 nasta.setSurname("Spotakova");
18 repository.save(nasta);
19
20 repository.findById(2L).ifPresent(p -> LOGGER.info("Find by id 2: {}", p));
21 repository.deleteById(2L);
22
23 LOGGER.info("Count Person records: {}", repository.count());
24
25 repository
26 .findOne(new PersonSpecifications.NameEqualSpec("John"))
27 .ifPresent(p -> LOGGER.info("Find by John is {}", p));
28
29 persons = repository.findAll(new PersonSpecifications.AgeBetweenSpec(20, 40));
30
31 LOGGER.info("Find Person with age between 20,40: ");
32 persons.stream().map(Person::toString).forEach(LOGGER::info);
33
34 repository.deleteAll();
Program output:
Count Person records: 4
Person [id=1, name=Peter, surname=Sagan, age=17]
Person [id=2, name=Nasta, surname=Kuzminova, age=25]
Person [id=3, name=John, surname=lawrence, age=35]
Person [id=4, name=Terry, surname=Law, age=36]
Find by id 2: Person [id=2, name=Barbora, surname=Spotakova, age=25]
Count Person records: 3
Find by John is Person [id=3, name=John, surname=lawrence, age=35]
Find Person with age between 20,40:
Person [id=3, name=John, surname=lawrence, age=35]
Person [id=4, name=Terry, surname=Law, age=36]
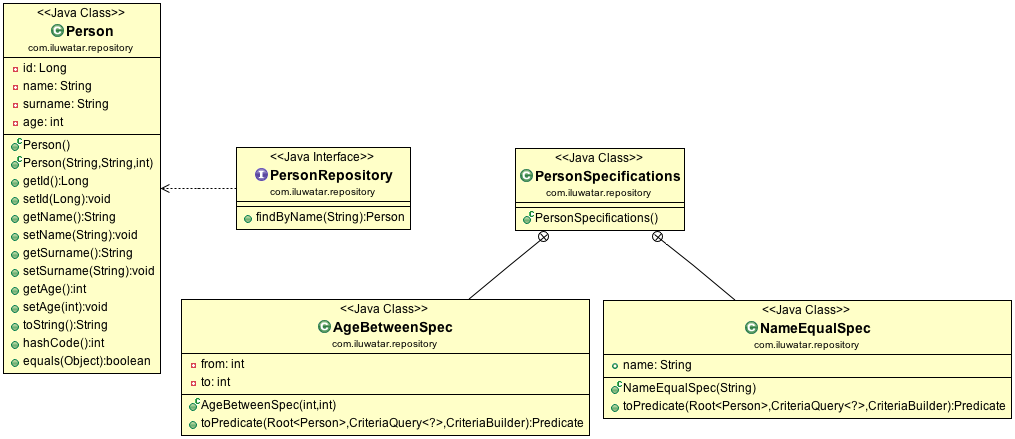
Class diagram
Applicability
Use the Repository pattern when
- The number of domain objects is large.
- You want to avoid duplication of query code.
- You want to keep the database querying code in single place.
- You have multiple data sources.